What is Gout?
GOUT CONDITION
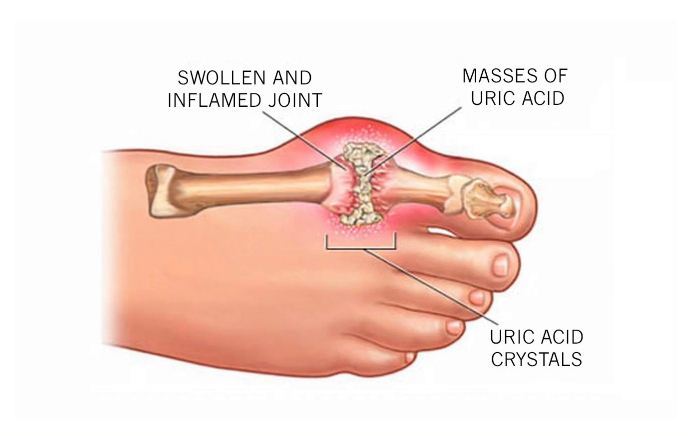
Gout is caused by abnormal metabolism of substances called purines that result in the accumulation of uric acid in the bloodstream. Purines are a by-product of cell break down. When the excretion of the uric acid is hampered the accumulated uric acid in the bloodstream causes crystalline deposits to form in joints or in the soft tissues. When this happens, there is a sudden onset of extreme pain with associated swelling, redness, and increased warmth to the skin or joint. Classic gout occurs in the big toe joint. It also commonly occurs in the knee joint. Rarely is it seen in more than one joint at a time. Uric acid accumulation in other joints and areas of soft tissue is less common. When gout presents in these areas it, may not be recognized as gout by the treating doctor. .
What Causes Gout?
Factors that contribute to the onset of gout are alcohol, red meats, aspirin and certain medications for high blood pressure. Gout occurs most frequently in men. Women will not get gout until after menopause unless they have had a hysterectomy. Patients with long-standing diabetes who may have kidney damage due to their disease and patients who have kidney disease from other causes can develop gout. These patients may exhibit atypical forms of gout. In these instances, more than one area may be affected; the tops of both feet, for example, may develop gout.
Typically the onset of gout is sudden and intense. Frequently, the patient will go to bed feeling fine and wake up the next morning in excruciating pain. The attacks can become recurrent, and over time cause permanent damage to the affected joint (arthritis). Recurrent gout should be treated with medication to reduce the blood uric acid levels. The most common medication used is Allopurinol. This medication should not be started during an acute attack. If this medication is given during an acute attack it will make the condition worse. Acute attacks of gout are treated with a variety of prescription anti-inflammatory drugs.
Gout Condition Diagnosis
Tests to help diagnose gout may include:
- Joint fluid test. Your doctor may use a needle to draw fluid from your affected joint. Urate crystals may be visible when the fluid is examined under a microscope.
- Blood test. Your doctor may recommend a blood test to measure the levels of uric acid and creatinine in your blood. Blood test results can be misleading, though. Some people have high uric acid levels but never experience gout. And some people have signs and symptoms of gout but don’t have unusual levels of uric acid in their blood.
- X-ray imaging. Joint X-rays can be helpful to rule out other causes of joint inflammation.
- Ultrasound. Musculoskeletal ultrasound can detect urate crystals in a joint or in a tophus. This technique is more widely used in Europe than in the United States.
- Dual-energy CT scan. This type of imaging can detect the presence of urate crystals in a joint, even when it is not acutely inflamed. This test is not used routinely in clinical practice due to the expense and is not widely available.
Gout Treatment
Treatment for gout usually involves medications. What medications you and your doctor choose will be based on your current health and your own preferences. Gout medications can be used to treat acute attacks and prevent future attacks. Medications can also reduce your risk of complications from gout, such as the development of tophi from urate crystal deposits.
Typically the onset of gout is sudden and intense. Frequently, the patient will go to bed feeling fine and wake up the next morning in excruciating pain. The attacks can become recurrent, and over time cause permanent damage to the affected joint (arthritis). Recurrent gout should be treated with medication to reduce the blood uric acid levels. The most common medication used is Allopurinol. This medication should not be started during an acute attack. If this medication is given during an acute attack it will make the condition worse. Acute attacks of gout are treated with a variety of prescription anti-inflammatory drugs.
Our Board Certified Podiatrists
Socal Foot and Ankle doctors are committed to delivering the most exceptional treatments.

Board Certified Foot & Ankle Specialist
Office Time
Location: Santa Monica
Mon – Thur: 9:00 AM – 5:00 PM
Friday: 9:00 AM – 5:00 PM
Location Marina Del Rey
Mon – Thur: 9:00 AM – 5:00 PM
Friday: 9:00 AM – 5:00 PM
Location: Cedars Sinai
Mon – Thur: 9:00 AM – 5:00 PM
Friday: 9:00 AM – 5:00 PM

Board Certified Foot & Ankle Specialist
Office Time
Location: Santa Monica
Mon – Thur: 9:00 AM – 5:00 PM
Friday: 9:00 AM – 5:00 PM

BOARD CERTIFIED
FOOT & ANKLE
Surgeons
- Comprehensive Treatment of Foot & Ankle Conditions in the Pediatric, Adult & Geriatric population
- 3 Practice Locations Santa Monica Medical Plaza, Cedars Sinai Medical Towers, & UCLA Health in Marina Del Rey
- On Staff with Providence Saint Johns Health Center &Cedars Sinai Medical Center
