SESAMOID BONES
What are Sesamoids?
A sesamoid is a bone embedded in the tendons that course below your big toe joint. Sesamoids are found in several joints in the body. Your kneecap, or patella, is another example. Acting as a fulcrum news essays point, the sesamoids help the big toe move normally and provide leverage when the big toe “pushes off” during walking and running. The sesamoids also serve as the weight-bearing interface for the first metatarsal bone. As such, they absorb the weight placed on the ball of the foot in motion. Sesamoid injuries encompass a variety of disorders involving tendons, bones, ligaments and/or surrounding tissues.
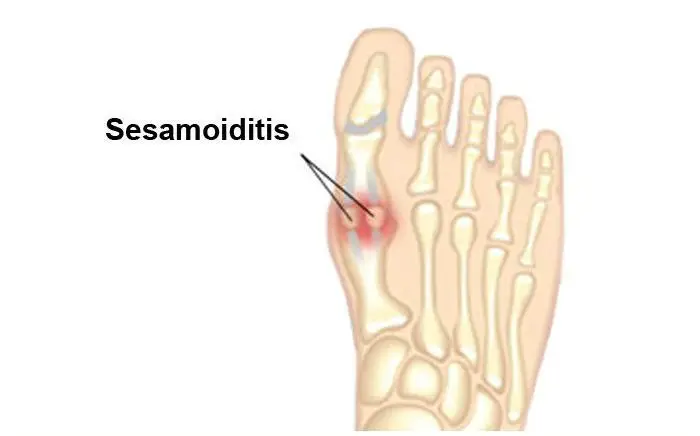
Sesamoiditis is an inflammatory condition of the periosteum or bone lining of the sesamoid bone. Typically, patients will relate a history of excessive activity as a precursor to pain in this location. Other risk factors include: running, jumping from a height, ballet dancing, wearing of high heels or shoes with little cushioning and high-arched foot type. With early and appropriate treatment, these often improve.
What Are The Symptoms?
- Pain is focused under the great toe on the ball of the foot. With sesamoiditis, pain may develop gradually; with a fracture, the pain will be immediate.
- Swelling and bruising may or may not be present.
- You may experience difficulty and pain in bending and straightening the great toe.
Diagnosis
Initial diagnosis is made by a careful history and physical examination. Pain localized to the bottom of the great toe joint is the typical presentation of these types of injury. The pain can be easily localized to either the tibial or fibular sesamoid by directly pressing on either bone. Movement of the joint may also duplicate the patient’s pain.
Occasionally, swelling and redness may also be seen depending on the mechanism of injury. X-rays are often obtained to differentiate sesamoiditis from a sesamoid fracture. Three different views of the sesamoids are commonly taken. Also, when sesamoid fractures are suspected, it is helpful to x-ray the uninvolved side as well.
Typically, the sesamoid bones are 2 well-defined bones on x-ray. This is the case for approximately 85% of the population. However, in 15% of patients, each sesamoid bone may consist of 2 or more fragments (referred to as multipartite – several pieces). This will often make the distinction between normal and fracture difficult. In this case, a bone scan or MRI can be helpful. It is important to differentiate between sesamoiditis versus fracture since the treatment is dramatically different.
Treatment
The treatment of sesamoid injuries is dependent on making a definitive diagnosis. Because sesamoiditis is an inflammatory condition, treatment directed at reducing inflammation is often helpful. This may include rest, ice, anti-inflammatory medications, and physical therapy. More resistant cases of sesamoiditis may be helped by occasional cortisone injection. These should only be performed after the physician is fairly certain a fracture does not exist.
Long-term therapy must be geared to identifying the cause of the sesamoiditis so as to avoid these situations or to accommodate foot deformities or modify shoes. This may include the use of orthotic devices. This may also include the limited use of high heel shoes.
Sesamoid fractures require a more aggressive course of treatment because of the high risk of nonunion. Cast immobilization for 6-8 weeks is the initial treatment of choice. The patient should then be advanced gradually to full weightbearing with a removable brace. Even in spite of appropriate treatment, many sesamoid fractures go on to delayed or non-unions. When conservative care has failed to render the patient pain free, consideration to removal of the offending sesamoid should be given. Once again, long-term therapy should be geared at identifying the cause of the fracture and treating or modifying those activities leading to the fracture in the first place.
Our Docters
Our Board Certified Podiatrists
Socal Foot and Ankle doctors are committed to delivering the most exceptional treatments.

Board Certified Foot & Ankle Specialist
Office Time
Location: Santa Monica
Mon – Thur: 9:00 AM – 5:00 PM
Friday: 9:00 AM – 5:00 PM

Board Certified Foot & Ankle Specialist
Office Time
Location: Santa Monica
Mon – Thur: 9:00 AM – 5:00 PM
Friday: 9:00 AM – 5:00 PM
Request Appointment
NON-INVASIVE ADVANCED TREATMENT
BOARD CERTIFIED
FOOT & ANKLE
Surgeons
Years Experience
Happy Patients
Location
Local Partners
